How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill increasingly sought after. This guide provides a comprehensive overview, from pre-flight checks and legal considerations to mastering drone controls and capturing stunning aerial footage. We’ll explore various aspects, ensuring you understand the technicalities and safety protocols necessary for responsible drone operation. This journey will equip you with the knowledge to confidently navigate the skies.
We’ll cover everything from understanding your drone’s controls and navigating complex environments to mastering camera settings and optimizing battery life. Safety is paramount, so we’ll emphasize pre-flight checks, legal regulations, and emergency procedures. By the end, you’ll be ready to take to the skies with confidence and skill.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
A thorough pre-flight check is crucial for safe and successful drone operation. This involves inspecting various drone components and ensuring compliance with regulations. Neglecting this step can lead to accidents, damage, and legal repercussions.
Drone Pre-Flight Inspection
Before each flight, perform a comprehensive inspection of your drone. This ensures all systems are functioning correctly and minimizes the risk of malfunctions during operation.
| Component | Check | Acceptable Result | Unacceptable Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Inspect for damage, cracks, or imbalance. | Propellers are intact and balanced. | Propellers are damaged, cracked, or unbalanced. Replace immediately. |
| Battery | Check battery level and ensure it’s properly connected. | Battery is sufficiently charged and securely connected. | Battery is low or not connected properly. Charge or reconnect. |
| Camera | Verify camera functionality and lens clarity. | Camera is functioning correctly, lens is clean and clear. | Camera is malfunctioning or lens is dirty or damaged. Clean or repair. |
| GPS Signal | Confirm a strong GPS signal is acquired. | GPS signal is strong and stable. | Weak or no GPS signal. Relocate to an area with better reception. |
| Gimbal | Check gimbal movement and stability. | Gimbal moves smoothly and is stable. | Gimbal is stiff, jerky, or unstable. Check for obstructions or calibration issues. |
| Flight Controller | Ensure all lights and indicators are functioning as expected. | All lights and indicators operate normally. | Abnormal light patterns or indicators. Check for connection issues or software problems. |
Understanding Drone Regulations and Airspace Restrictions
Operating a drone without understanding and adhering to local regulations can result in hefty fines, license suspension, or even criminal charges. Familiarize yourself with the specific rules in your area before each flight.
For example, flying near airports or restricted airspace is strictly prohibited in most jurisdictions. Failure to comply can lead to significant penalties and potentially endanger air traffic.
Safe Flight Zone Visualization
Imagine a circular flight zone, with the drone at the center. The zone is color-coded: a green inner circle represents the primary flight area, free from immediate obstacles. A yellow outer ring indicates a caution zone, where potential hazards like trees or buildings exist, requiring careful maneuvering. A red outer ring defines the absolute no-fly zone, encompassing areas like roads, people, or restricted airspace.
Wind direction is indicated by an arrow, and a designated area within the green circle marks a potential emergency landing spot. Obstacles are marked with black symbols, while the wind direction is shown with a blue arrow.
Drone Controls and Navigation: How To Operate A Drone
Understanding your drone’s controls is fundamental to safe and effective operation. Different control modes cater to various skill levels and flight scenarios.
Basic Drone Controls
- Throttle: Controls the drone’s altitude. Pushing the stick up increases altitude, pushing it down decreases altitude.
- Yaw: Controls the drone’s rotation around its vertical axis (turning left or right).
- Pitch: Controls the drone’s movement forward and backward.
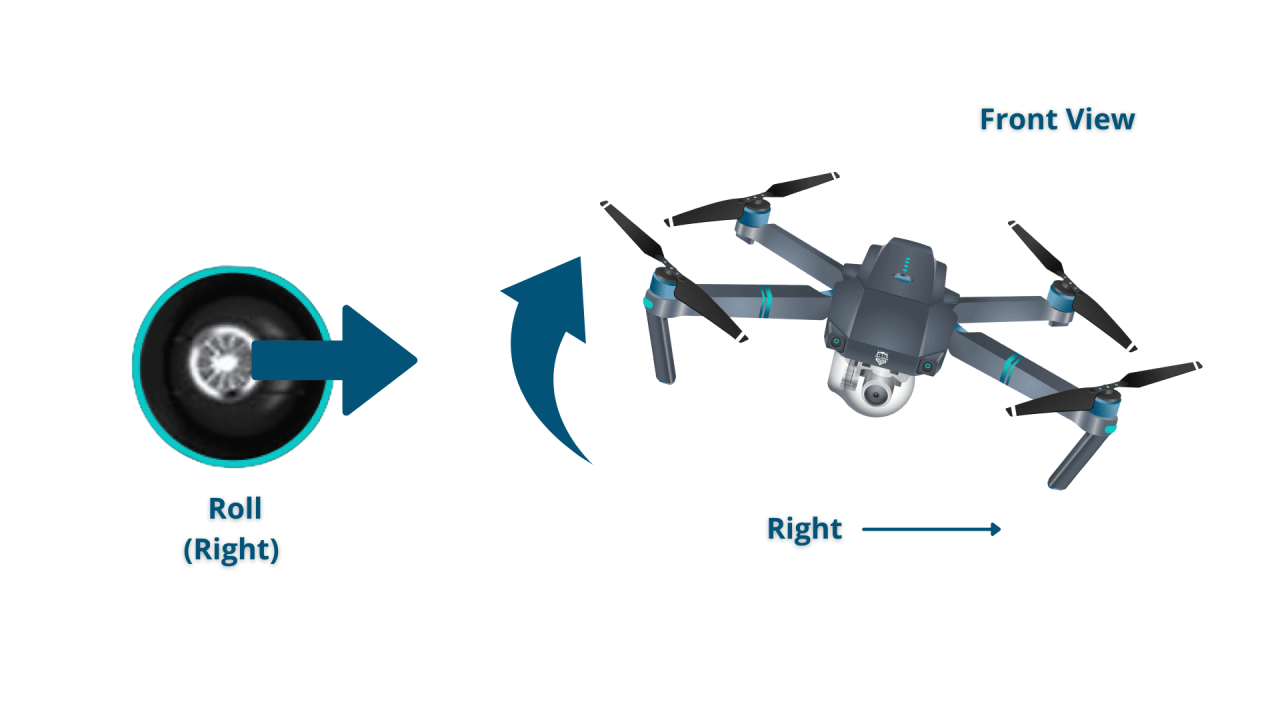
- Roll: Controls the drone’s movement left and right (sideways).
Drone Control Modes
Beginner mode typically limits the drone’s speed and responsiveness, preventing abrupt movements. Expert mode unlocks full control, allowing for faster speeds and more complex maneuvers. GPS mode uses satellite data for precise positioning and stability, particularly useful for longer flights or complex shots.
Understanding drone operation involves several key aspects, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. Successfully piloting a drone requires mastering the controls and understanding its limitations. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone and learn how to safely and effectively operate your drone.
Safe and responsible drone operation is paramount for both personal safety and legal compliance.
Beginner mode offers safety and ease of use but limits maneuverability. Expert mode provides full control but requires skill and practice to avoid accidents. GPS mode enhances stability and precision but relies on a clear GPS signal.
Navigating a Complex Obstacle Course
- Assess the course, identifying all obstacles and planning a safe flight path.
- Begin at a safe distance, gradually approaching the first obstacle.
- Use precise movements of the pitch and roll controls to navigate around obstacles, maintaining a safe altitude.
- Adjust yaw as needed to maintain the desired flight path.
- Continuously monitor the drone’s position and battery level.
- Practice slow and controlled movements to ensure precise maneuvering.
Camera Operation and Image Capture
Understanding camera settings and modes is key to capturing high-quality aerial footage. Different settings and modes are suitable for various shooting scenarios.
Camera Settings Adjustments
ISO controls the camera’s sensitivity to light. Higher ISO values are useful in low-light conditions but can introduce noise. Shutter speed determines how long the camera’s sensor is exposed to light. Faster shutter speeds freeze motion, while slower speeds can create motion blur. Aperture controls the size of the lens opening, affecting depth of field and light intake.
A wider aperture (smaller f-number) creates a shallower depth of field, blurring the background, while a narrower aperture (larger f-number) increases depth of field, keeping both foreground and background in focus.
Camera Modes
Photo mode captures still images. Video mode records moving footage. Timelapse mode captures a series of images at set intervals, which can be compiled into a time-lapse video. Photo mode is ideal for capturing sharp, detailed images of landscapes or buildings. Video mode is perfect for recording events or creating cinematic aerial shots.
Timelapse mode is great for showcasing changes over time, such as cloud movements or the progression of a construction project.
Aerial Footage Plan: City Skyline
To capture a stunning city skyline, start by selecting a location with minimal obstructions and good visibility. Fly at a safe altitude, maintaining a distance from buildings and other structures. Use a wide-angle lens to capture the entire skyline. Employ a slow panning motion to showcase the city’s expanse. Consider using a combination of photo and video modes to capture both detailed stills and dynamic footage.
Optimize camera settings for optimal light exposure and clarity. For example, use a relatively low ISO value to minimize noise and a shutter speed that avoids motion blur.
Battery Management and Flight Time
Proper battery care extends the lifespan of your drone’s battery and ensures optimal flight time. Understanding battery characteristics and managing flight time are crucial for safe and efficient drone operation.
Understanding drone operation involves grasping several key concepts, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. Learning the basics is crucial for safe and responsible flying, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone which covers everything from controls to emergency procedures. Ultimately, mastering how to operate a drone requires practice and a commitment to safety.
Battery Care and Maintenance

Always charge your batteries using the recommended charger and follow the manufacturer’s instructions. Avoid overcharging or discharging the batteries completely. Store batteries in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight or extreme temperatures. Regularly inspect batteries for any signs of damage or swelling.
Drone Battery Comparison
| Battery Type | Flight Time (approx.) | Charge Time (approx.) |
|---|---|---|
| Intelligent Flight Battery 1 | 25 minutes | 60 minutes |
| Intelligent Flight Battery 2 | 35 minutes | 90 minutes |
| Intelligent Flight Battery 3 | 45 minutes | 120 minutes |
Note: Flight times are approximate and can vary depending on factors such as weather conditions, drone load, and flight style.
Calculating Remaining Flight Time, How to operate a drone
To estimate remaining flight time, monitor the battery percentage displayed on your drone’s controller or app. Consider the battery’s typical flight time and adjust the estimate based on your current flight style (aggressive maneuvers consume more power). For instance, if your battery typically provides 30 minutes of flight time and is at 50%, you have approximately 15 minutes of flight time remaining.
Troubleshooting Common Issues

Understanding common drone malfunctions and their solutions enables quick problem-solving and minimizes disruptions. Knowing how to handle emergencies is crucial for safe drone operation.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Troubleshooting
Several issues can arise during drone operation. Here’s how to address some of the most common ones:
Loss of Signal
- Check the distance between the drone and the controller. Ensure you’re within the controller’s operational range.
- Check for obstructions between the drone and the controller, such as buildings or trees.
- Try restarting both the drone and the controller.
- If the problem persists, check for firmware updates or contact technical support.
Low Battery
- Check the battery level on your controller or app.
- Land the drone immediately if the battery level is critically low.
- Charge the battery fully before the next flight.
GPS Issues
- Ensure the GPS signal is strong and stable. Relocate to an area with better reception if necessary.
- Check for obstructions that might be interfering with the GPS signal.
- Restart the drone and try again.
- Calibrate the GPS if necessary.
Emergency Procedures
In case of loss of control, immediately attempt to regain control using the available controls. If unsuccessful, prioritize a safe landing, selecting a clear and unobstructed area. If a safe landing isn’t possible, consider using the emergency stop function (if available) to bring the drone down.
Mastering drone operation is a rewarding experience that blends technology, skill, and creativity. This guide has provided a foundational understanding of the necessary steps, from pre-flight preparation to post-flight analysis. Remember that consistent practice, adherence to safety regulations, and a respect for airspace are key to becoming a responsible and proficient drone pilot. Soar safely, and enjoy the breathtaking perspectives that await you.
Quick FAQs
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with GPS and beginner modes are ideal for starting. Look for features like automatic return-to-home and obstacle avoidance.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Calibrate your compass before each flight, especially if you’ve moved significantly from your previous flight location or experienced interference.
What should I do if I lose signal with my drone?
Most drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function. Activate this immediately. If unavailable, try to regain signal by moving to a higher vantage point. If signal remains lost, locate your drone visually.
How do I clean my drone’s camera lens?
Use a microfiber cloth and lens cleaning solution specifically designed for camera lenses. Avoid harsh chemicals or abrasive materials.
